Cybersecurity simulation training: a definition
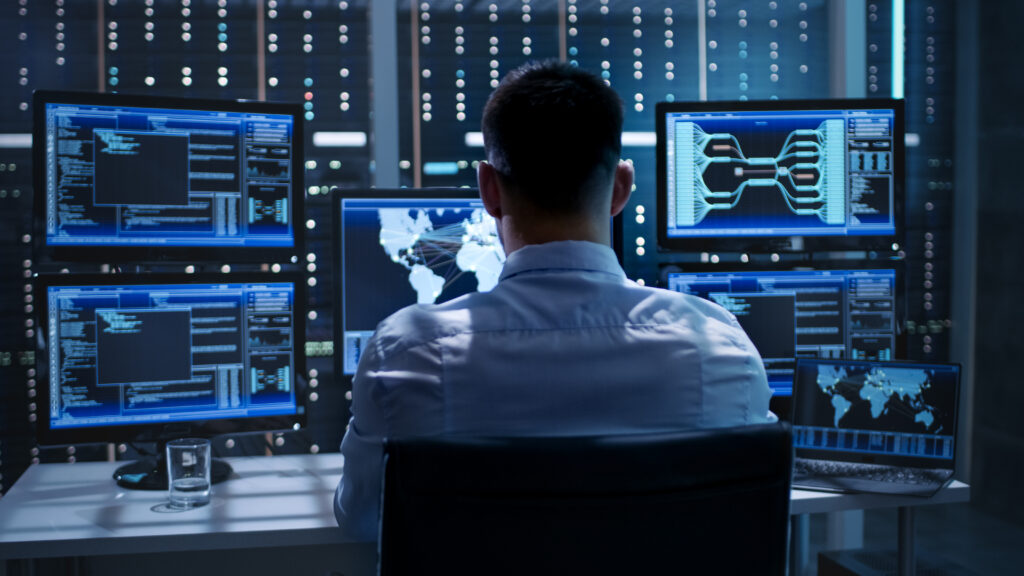
Cybersecurity simulation training is a way to accurately replicate your IT setup and test how your organization responds to simulated cyberattacks. By replicating your environment, you can effectively “war-game” against potential attacks in realistic scenarios.
Not only does this provide your IT professionals and security staff with real-life experience, but you can see how your defenses and strategy would hold up against an actual attack.
With the option to choose between a wide range of incident scenarios of varying severity, you can provide hands-on training that will give you the edge against cybercriminals.
The need for cybersecurity hands-on training
As businesses of all sizes now face a higher frequency and sophistication of cybercrime, there has been a shift in how seriously businesses take the threat. With the very real possibility of financial and reputational damage, businesses have been looking at a variety of different ways to sure up their defenses. These range from IT investment, recruiting specialist security staff, partnering with cybersecurity experts, and training.
Training has been at the forefront of many cybersecurity strategies, but there is a lot of room for improving the scope and effectiveness of this training. Teaching users about the importance of strong passwords and how to identify phishing attacks is a valuable exercise. However, users across the organization, not just the specialists in IT, need to know what to do when a cyberattack occurs. Reacting in the right way at the right time could save your organization from worst-case scenarios.
For this, there is a great need for rigorous cybersecurity hands-on training. There are many different names given to these types of simulation environments, such as cyber range training, virtual cybersecurity labs, and cybersecurity practice labs. However, all of these different terms amount to the same thing. They all offer real-world, hands-on cybersecurity training that provides staff with real experiences of dealing with the complexities of a cyberattack.
The importance of cybersecurity practice labs
Everyone’s accustomed to practicing for fire drills and other emergencies in the workplace. Why not cybersecurity simulation training, too? When cyberattacks are approached in the same way, everyone has real-life experience of how to react. The greatest benefits of cybersecurity simulation training will be realized by IT professionals and security staff, who can probe and test every aspect of their organization’s cybersecurity setup to see what holds up when it’s under attack. But, as everyone has a role to play, it can pay dividends to get everyone involved across the organization.
The benefits of cybersecurity training simulators
- Real-life experiences – You can’t beat learning that comes from real-life experiences. By training people in cybersecurity practice labs, you can improve training efficiency and reduce costs.
- Test strategies and new technology safely – Have you developed a new strategy to fight off the latest threat or invested in new security technology? Cybersecurity practice labs allow you to test these in a safe environment, i.e., to test out a realistic simulation of your IT networks rather than damaging the networks themselves. Likewise, cyber range training can be used to test new staff or be used during interviews to ensure new candidates have the right skills or mindset for important security roles.
- Gain crucial insights from data – Because cybersecurity simulation training uses simulations of your real IT environment, you can gain lots of valuable data while you train your staff. Not only can this be used to improve and guide training, but it can also be used to gain insights about how and where to invest in IT security.
- Offer training organization-wide – Train the entire organization and empower your people to help defend against the biggest and smallest threats. With hands-on training, employees can better understand what is required of them, whether they are cybersecurity experts, part of the C-suite, or a line-of-business worker.
- Create a cybersecurity culture – Following from the previous point, when everyone is engaged in cybersecurity you can radically improve how people think and talk about cybersecurity, but also, most importantly, how they act when an attack occurs.